| HOME |
| CUSTOM DESIGN |
| PRODUCTS |
| CONTACT |
| CIRCUITS |
| FAQs |
| RESOURCES |
| LINKS |
| ABOUT |
|
Each of the 16 outputs can
be connected through a resistor and then through an LED to serve as a
simple 16 LED controller. The LED can be chosen at random by the status
of the 4 line selector inputs. However, due to the internal structure
of the 74154, only one output can be enabled at a time. This chip is
often used in demultiplexing applications, such as digital clocks, LED
matrices, and other graphical outputs. For example, if the target
application requires 16 7-segment LED displays, but your
microcontroller only has 4 lines to select which display is active,
this chip (74LS154) would provide a very effective method of
essentially multiplying you selecting lines by a 4 times. Understand,
this is a typical example of application, not it's sole purpose.
Download the datasheet below for a more comprehensive summary.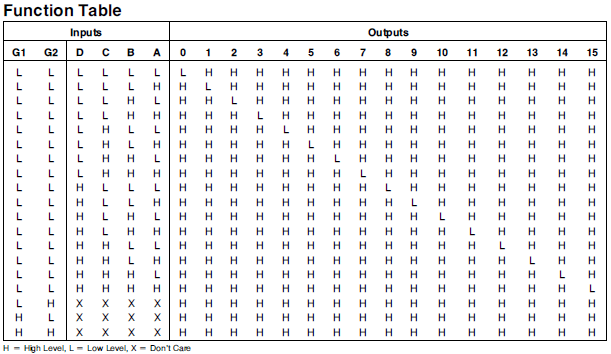 |
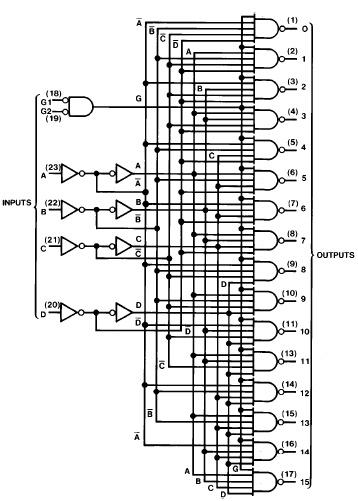
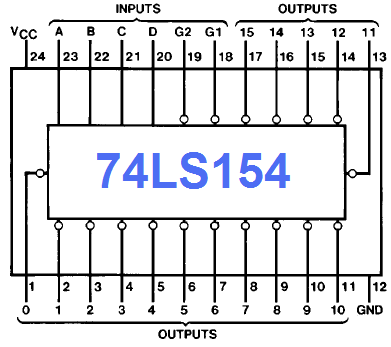 Each or these 4-line-to-16-line decoders
utilizes TTL circuitry
to decode four binary-coded inputs into one of sixteen mutually exclusive outputs when both the strobe inputs, G1 and G2, are low. The demultiplexing function is performed by using the 4 input lines to address the output line, passing data from one of the strobe inputs with the other strobe input low. When either strobe input is high, all outputs are high. These demultiplexers are ideally suited for implementing high-performance memory decoders. All inputs are buffered and input clamping diodes are provided to minimize transmission-line effects and thereby simplify system design. |
 |
| 74154 DATASHEET |
||