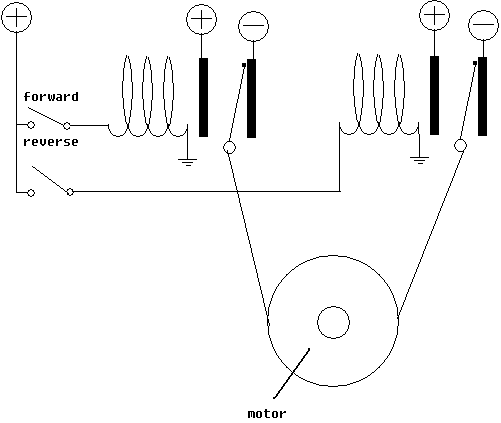
The relays in the schematic above are in their normal state. With no power applied to the electromagnets, both terminals of the motor remain grounded. Depending on what relay is triggered the motor can be spun either forward or reverse. An electromagnetic breaking effect will occur when both terminals are connected. When either both relays are either enabled or disabled the motor will break. In this circuit there is no idle. The motor will quickly come to a stop once power is removed from the relays. Since a DC electric motor can also act as a generator, electricity will continue to be produced after the battery is removed and the motor slows down. The breaking effect occurs when this generated electricity is fed back into the motor (by the motor terminals being directly connected). Another way to think of this phenomenon is as electromagnetic friction.